Air filtration
Contents |
[edit] Introduction
The process of air filtration uses filters to capture and remove particles from the air.
The purpose of air filtration is to reduce contaminants from entering buildings (or parts of buildings) and to improve indoor air quality (IAQ) and airborne hygiene levels. Certain types of air filtration technology can be incorporated directly into heating ventilation and air conditioning (HVAC) systems to remove contaminants from outdoor air that has been brought for ventilation.
In some cases, air filtration is used to reduce the amount of outdoor air that may be required for ventilations by recirculating internal air mixed with some 'fresh' air. However, as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic, recommendations regarding recirculation have been changed.
The type of contaminant being captured will influence the suitability of different air filtration systems.
[edit] Air filters for buildings
Air filters are systems or components that remove particulates from the air as it passes through filtering elements. Some of the most common types of filtering elements include fabric (those made from woven and felted fabrics that are used to collect particles on their surface) and fibrous (those fabricated out of a mat of non-woven fibres such as fibreglass and various polymers; these are then incorporated into filters that collect particles throughout their structure).
Other types of contaminants require transformation (into harmless substances) through a process of a chemical reaction, or processes such as the application of ultraviolet light. In some instances, electrostatic attraction and gravitational settling may also contribute to particle capture.
[edit] Types of air filtration systems
Common types of air filtration systems include:
- Mechanical and electronic air filters. These devices remove particles by generating electrical fields and/or ions and passing the charged air through a filtering agent (also known as filter media). Some filters use a static electrical charge to increase collection and removal of particles. In large systems, the measurement of particles removed may be referred to as particle removal efficiency, filter efficiency or single-pass efficiency based on the minimum efficiency reporting value (MERV). In portable systems, the measurement is referred to as the clean air delivery rate (CADR).
- Sorbent air cleaners. Sorbent air cleaners are primarily used to remove harmful gaseous contaminants from airstreams. They use a process that involves physical adsorption (with materials such as activated carbon) along with chemisorption. There is frequently a combination of different types of air filtration systems in place when sorbent air cleaning is used.
- Photocatalytic oxidation (PCO) air cleaners. This is a reaction between gases and biological particles on certain semiconductor or photocatalyst materials such as TiO2 (titanium dioxide). The addition of other substances may improve the performance of photocatalysts, and various ultraviolet light sources may also be used in this process.
- Ultraviolet (UV-C) germicidal irradiation (UVGI). This air cleaning technique uses ultraviolet light to treat viruses, bacteria and fungi by degrading organic material in the airstream. This does not remove the contaminants - it merely deactivates them. This technique can be used inside HVAC systems or can be used as a portable air cleaning device. It is also used in some swimming pools.
- There are also combination air cleaning packages that incorporate multiple air filtration approaches. These technologies may be portable with several types of filters as well as fans.
See also: Types of air filter.
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings
- Air filtration and clean indoor air quality standards.
- American Society of Heating and Air-conditioning Engineers.
- Arrestance.
- Building regulations.
- Clean air delivery rate CADR.
- Clean indoor air for healthy living - New air filter standards.
- Designing HVAC to resist harmful microorganisms.
- Growing focus on IAQ challenges for specifiers and HVAC manufacturers.
- Heating ventilation and air conditioning HVAC.
- High efficiency particulate arrestance HEPA.
- Indoor air quality.
- Let us evolve our buildings from being passive structures to interactive and reactive systems.
- Minimum efficiency reporting value MERV.
- Types of air filter.
- Ventilation and control of COVID-19 transmission.
[edit] External resources
- Illustrated Guide to Ventilation (BG 2/2009), compiled by Kevin Pennycook and published by BSRIA in 2009.
- American Society of Heating and Air-conditioning Engineers (ASHRAE), ASHRAE Position Document on Filtration and Air Cleaning.
- UK Scientific Advisory Group for Emergencies, Environmental and Modelling Group (SAGE-EMG), Potential application of Air Cleaning devices and personal decontamination to manage transmission of COVID-19.
- Science Direct, Assessing Nanoparticle Risks to Human Health by Peter C Raynor.
Featured articles and news
The first line of defence against rain, wind and snow.
Building Safety recap January, 2026
What we missed at the end of last year, and at the start of this...
National Apprenticeship Week 2026, 9-15 Feb
Shining a light on the positive impacts for businesses, their apprentices and the wider economy alike.
Applications and benefits of acoustic flooring
From commercial to retail.
From solid to sprung and ribbed to raised.
Strengthening industry collaboration in Hong Kong
Hong Kong Institute of Construction and The Chartered Institute of Building sign Memorandum of Understanding.
A detailed description from the experts at Cornish Lime.
IHBC planning for growth with corporate plan development
Grow with the Institute by volunteering and CP25 consultation.
Connecting ambition and action for designers and specifiers.
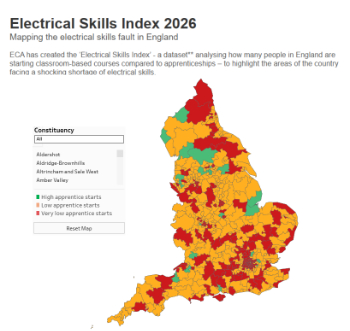
Electrical skills gap deepens as apprenticeship starts fall despite surging demand says ECA.
Built environment bodies deepen joint action on EDI
B.E.Inclusive initiative agree next phase of joint equity, diversity and inclusion (EDI) action plan.
Recognising culture as key to sustainable economic growth
Creative UK Provocation paper: Culture as Growth Infrastructure.
Futurebuild and UK Construction Week London Unite
Creating the UK’s Built Environment Super Event and over 25 other key partnerships.
Welsh and Scottish 2026 elections
Manifestos for the built environment for upcoming same May day elections.
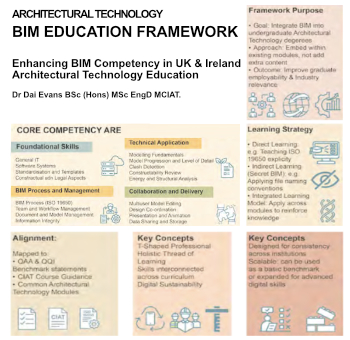
Advancing BIM education with a competency framework
“We don’t need people who can just draw in 3D. We need people who can think in data.”